Noise of intention in decision
It is a way to raise the quality of work as well as the product quality because it is the intention variation in the decision.
Let’s lead to business improvement and lead to profits.
What is variation?
The way of thinking of dispersion is important in considering quality as well as bias.
We will be involved in many things such as business efficiency improvement, business quality, business strategy, product image.
Variations in product manufacturing are very important items.
The way of thinking of variation in product manufacturing is detailed in this page.
“Variance and process capability”
What is variation in decision
Variation is “noise, difference between measurements”.
Especially in the case of this “decision making intention” it becomes a difference of way of thinking.
Actually there is something close to consistency thought.
As a result, this way of thinking will vary depending on time and individual.
Have not you felt like this in the company?
· Opinions differ depending on professionals
· Your boss’s decision is different each time (not stable)
It can be said that the variation of the way of thinking appears large.
It can be said that noise is great.
Differences in thinking, it comes out by time and individual
Should we manage the variation?
Should I actually manage that bias?
The idea here is exactly the same as intention bias in decision .
Let’s think about things at factories and other production sites.
Variation and Process Capability But we are talking in detail, but the product has variability / bias It is important to secure quality considering that.
As a result, there are standards in products, which will be passed to the world and the quality will be kept.
The way of variation as a natural phenomenon is represented by a normal distribution.
The deviation and variation of product manufacturing are as shown in the figure below.
The curve in blue is the ideal target distribution, the curve in red is a distribution with large variation, the curve in brown color is in distribution with bias.
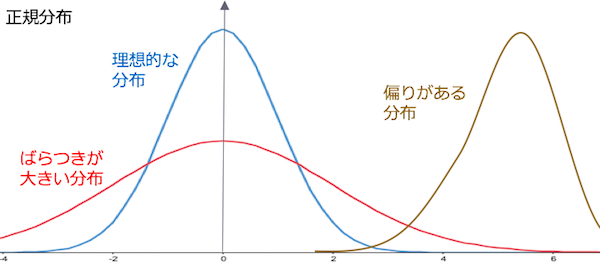
We will adjust it to approach the ideal target distribution.
This reduces reworking and disposal and improves profitability.
Exactly the same thing can be said in other work.
Manufacturers · factories say that this is the only way to secure quality and efficiency, but the business itself does not say much.
If you think that the object is central to the center, the ideal distribution in other tasks, the distribution with large dispersion, and the distribution with bias are as follows.
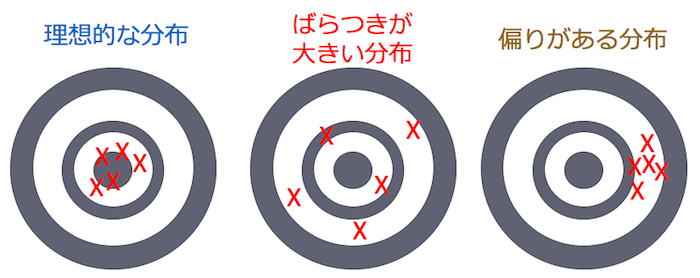
Depending on the work, there are few visible parts that are actually visible, and it is difficult to judge whether the quality is bad or bad.
However, it becomes very useful for the company by managing it.
Since the dispersion is a state of noise / difference distribution, it is necessary to modify as follows.
Efficiency improvement of work · Management is necessary for business quality assurance
The following book also details the way of thinking about business improvement in detail.
Please try it.
6ステップで職場が変わる! 業務改善ハンドブック
Types of variations in thinking
As I mentioned earlier, the variation is “noise / difference”.
There are several kinds of “noise / difference” in the way of thinking.
Variation with time
It will be a variation of ideas related to time.
The decision content for the same case also happens when the decision content differs if the time differs.
Although this is not the limit, I posted it as an example.
· Changes in attributes of the previous judgment material
· Change in will ability
· Changing mood of person in charge
Judgments and decisions are human.
Because it is a human being, it tends to change to decided contents due to the change of mood.
· When it’s fun → easily judge projects
· When you are angry → Judge relatively projects strictly
It may change like like.
· Changes in attributes of the previous judgment material
Differences will arise if the judgment remains unclear among the personnel responsible for the material whose judgment changes over time (change in amount of change and material itself).
· Changes in will ability
Although I mentioned during biasing, the ability to judge things firmly “Will power” will be exhausted in the same way as physical strength.
Because its will will be exhausted, it will be relatively accurate even if you make difficult judgments after waking up (usually in the morning if you work).
On the contrary, in the case of exhaustion (usually after work in the afternoon if you work) it is easy to make mistakes in your judgment.
“Variance” that occurs as judgment contents change with time
Individual variation
It becomes a variation of the way of thinking concerned among individuals.
It is a case that the decision content differs for people who are different for the same matter.
Here as well, this is not the limit, but I posted it as an example.
· Difference in judgment materials
· Difference in judgment method
– Character of person in charge
Even with the character of the person in charge, there are variations from case to case.
Compared with others
· Decision content is sweet → Easy judgment of projects
· Careful judgment → Judge relatively projects strictly
· Difference in judgment materials
Because judgment materials are different for each individual, judgment varies and variations in intention arise.
· Difference in judgment materials
· Grouping and segment differences
· Difference of each element
Accuracy and variation are born by the difference.
In order to approximate this to an ideal distribution,
· Difference in judgment method
The judgment differs depending on the individual judgment method, which causes variations in intention.
· Difference in priority
· Evaluation method
Work procedure
“Variance” that occurs when judgment contents change for individuals
Case of intention variation
There are no cases related directly to variation within the business.
Unlike bias, it is often caused by not only top judgment but also accumulation of fine parts.
First, I will introduce examples of intention variability as exercise.
The other one can not be said to involve variations in intention, but introduces examples in business that could be improved by modifying thinking and view.
Example of intention variation
As an example it will be the choice for the following situation.
Now you are looking for a job place.
Both You will be a company of industry and occupation you want to take.
The number and scale of employees are the same.
Which of the following companies would you like to work for?
Company ①
Average annual income: 8 million yen
Company ②
Average annual income: 6 million yen
Company ③
Average annual income: 5.5 million yen

Next, I will look at the contents of the company shown above.
It is when each company, the total number of employees is 10 people.
Company ① Annual income distribution with an average annual income of 8 million yen
2 million yen: 7 people
2 million yen: 2 people
60 million yen: 1 person
Company ② Annual income distribution with an average annual income of 6 million yen
2 million yen: 2 people
3 million yen: 1 person
7 million yen: 3 people
8 million yen: 4 people
Company ③ Annual income distribution with average annual income of 5.5 million yen
5.5 million yen: 10 people
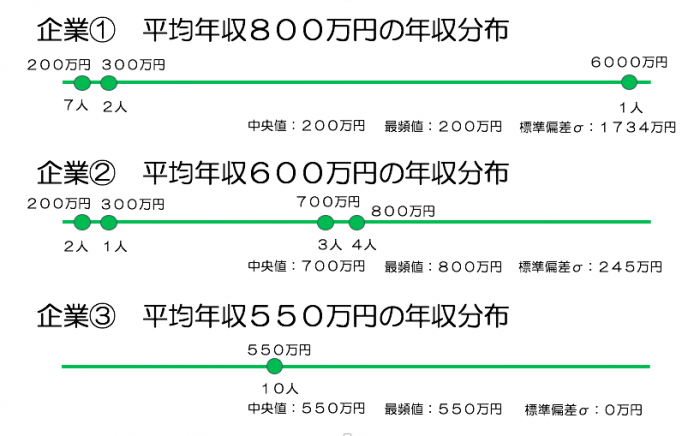
· Median: The annual income of the middle ranked person
· Mode: The annual income of those who apply the most
· Standard deviation σ: degree of noise
(Average value ± σ → range value of distribution of 68.3% of the whole)
I will ask you again.
Now you are looking for a job place.
Both You will be a company of industry and occupation you want to take.
The number and scale of employees are the same.
Which of the following companies would you like to work for?
Company ①
Average annual income: 8 million yen
Median value: 2 million yen
Mode: 2 million yen
Standard deviation: 17.34 million yen
Company ②
Average annual income: 6 million yen
Median value: 7 million yen
Mode: 8 million yen
Standard deviation: 2.45 million yen
Company ③
Average annual income: 5.5 million yen
Median value: 5.5 million yen
Mode: 5.5 million yen
Standard deviation: 0 million yen

Did you have any change in your intentions?
Have you included other judgment materials in the new information?
If there is a change it is also “variation” (noise, difference).
Judging materials are also important to get close to the ideal distribution.
The tendency of the group as a whole and the tendency when divided into groups may be different.
Materials of judgment that take them into account are also necessary.
If there was a change that also “variation”
Examples in Business – Regeneration of Japan Airlines –
It is a case of Japan Airlines (JAL).
Japan Airlines’ profit at the time of applying the Corporate Rehabilitation Act: March 2010 ▲ 133.7 billion (loss)
As a management method at that time, it roughly looks like the following.
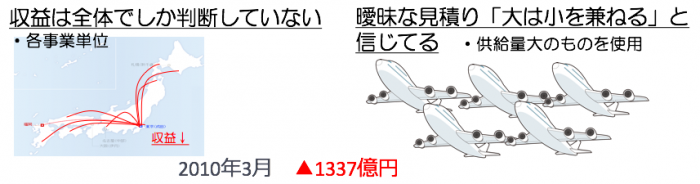
· Revenue is judged only on the whole in each business unit
· Ambiguous estimation We thought that “Da is small”
→ Variation in management judgment was great
Kazuo Inamori started regenerating Japan Airlines and improved it as follows.
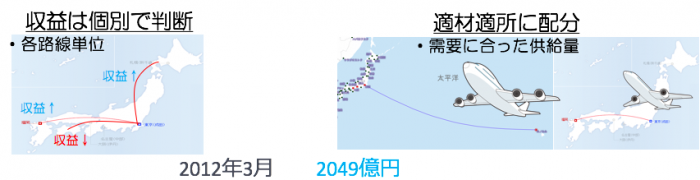
· Revenue is determined individually
· Allocate to the right place
→ We decided to use individual judgment criteria by using appropriate judgment materials for business judgment.
Profit after two years from the application of the Corporate Rehabilitation Law: March 2012 ¥ 204.9 billion (surplus)
As management judgment approaches an ideal distribution, it can be said that the result was derived as a profit.
Clarified judgment materials and information, I approached ideal distribution according to individual criteria
To avoid variations
How do I avoid variations?
First, I will explain the concept of basic variation avoidance and the decision algorithm to avoid variation.
Concept of basic variation avoidance
Having a basic idea will reduce the dispersion to a certain extent and the judgment will approach the ideal distribution.
· common information
Variance will increase if you have different information.
If we collect information acquired by individual, we will share it and make it common information.
On the contrary, let’s have a system that can accept common information.
· common judgment material
As I mentioned in the previous example, in order to bring it closer to an ideal distribution with less variation, it is necessary to have a judgment material suitable for it.
For that reason, we must consider the relationship of judgment materials to the quality of the project.
Of course, I think that there is also a related direction in the positive direction if there is also a related direction in the minus direction, but I put both.
In addition, we will use judgment materials as common recognition without changing.
Even if there is common information, common judgment method if it changes, it differs.
· Common judgment method
By deciding the common judgment method, it will be difficult for differences to appear in the judgment difference.
· Clarify procedures
· Clarify priorities
· Clarify judgment criteria of evaluation method
Let’s do common methods such as.
Common information, common judgment materials, judgment method are necessary to reduce the variation
Judgment algorithm for avoiding variation
Common judgment materials and judgment methods are necessary to avoid variations.
However, judgment is often difficult.
This will be a useful way.
This method can be judged logically by giving “rare degree” of appearance to judgment material as a numerical value.
Moreover, this method can compare even if there is no unit of judgment material.
- List six or more items related to results
- Obtain average value and standard deviation for each item from a certain amount of past data
- Issue the value you want to evaluate (the value of the opportunity)
- Apply “standard score” for each item for each item
- Issue “summary score” for each case
- Determine correspondence according to ranking of digest score, numerical value
– List six or more items related to results
I list six or more items that apply to common judgment materials.
Of course you can also include content related to minus direction.
(In that case, the coefficient for outputting the standard score is -1)
If judgment items change for a case, start from here.
There is no need to change it once you decide it.
Evaluate multiple items, example of comparison : Lunch selection (judgment item)
As an example, consider an example of choosing a menu for lunch.
In this case we will compare five types of deals (A lunch, B lunch, C lunch, ramen, curry).
I gave the following as a judgment item.
· Little people lined up
· Expected unit price
· Appearance deliciousness
· Calorie low
· Presence of events
· Low price
Each unit is different.

Next, average values and standard deviations for each item are output from past data.
· Generate average value / standard deviation for each item from a certain amount of past data
Calculate the average value and standard deviation value of the items listed above for a certain period of time.
Therefore, we can not do things that have no judgment materials in the past.
(I think that it can not be said that the judgment material is also related to the case that there is no value of judgment materials in the past, but,
Once you acquire the average value and standard deviation, there is no need to update frequently.
To use standard deviation in Excel, use “STDEV.P” function.
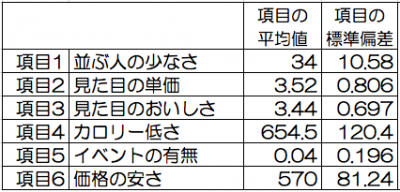
Examples of evaluating and comparing multiple cases : Selection of lunch (average value / standard deviation from past data)
I got it from the value of the item (menu) of the past week of each item.
The average value and standard deviation for each item are as follows.
Next, look at the value you want to evaluate.
· Get the value you want to evaluate (the value of the opportunity)
Fill in the value of the item for the case.
Since lunch selection is for multiple projects, if you want to evaluate one case you can fill in one column of example.
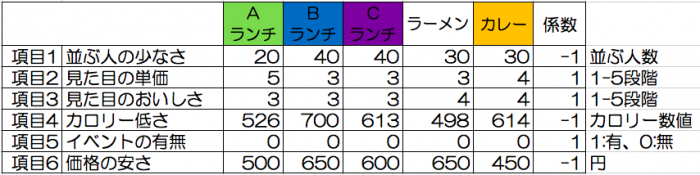
Evaluate multiple cases, example of comparison : Selection of lunch (value of case)
I will give out the evaluation value of today’s lunch menu.
For clarity, coefficients are also added here.
The coefficient “-1” is when the value of the item is better in the minus direction.
The value of this coefficient may be increased according to importance.
(However, please change when the judgment item changes for the case as for the change of the coefficient.)
This time it will be as follows.
I will give out a standard score from here.
· Issue “standard score” for each item for each item
Also, when you want to evaluate one case as well as “When evaluating and comparing multiple cases” also fill in the items, we will issue (item value x – mean value μ) / standard deviation σ for the item.
However, for items with negative judgment, multiply this calculation result by “-1”.
Also, depending on the importance of the item, multiply this calculation result by a factor. (Basically, you do not have to multiply the coefficient.)

Evaluate multiple cases, example of comparison : Selection of lunch (standard score)
For each item, we calculate the standard score “coefficient × (value x of project case – average value μ) / standard deviation σ”.
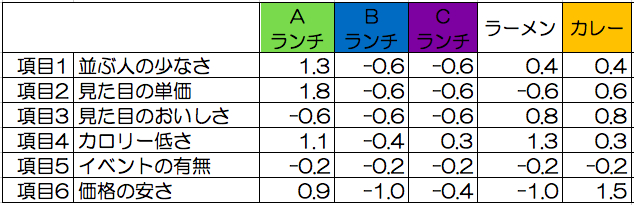
· Issue “summary score” for each case
Find the average value of the standard score for the case. (Standard score 1 + Standard score 2 + ⋯ + Standard score n) / Number of items n

Evaluate multiple cases, example of comparison : Selection of lunch (summary score)
We will calculate the average value for each item (for each menu) from the standard score you asked earlier.

– ranking of summary scores, determining responses according to numbers
We will make decisions based on summary score values.
· When you want to evaluate one case
Decision contents are decided for numerical value of summary score.
· When you want to evaluate and compare multiple items
Decision contents are decided for numerical value of summary score.
Alternatively, the determination content is determined with respect to the ranking of the numerical value of the summary score.
Evaluate multiple cases, example of comparison : Lunch selection (judgment)
I have decided the evaluation correspondence.
Here
Choose the highest summary score as lunch
Therefore, the judgment will be “A lunch”.
This reduced variance in choosing lunch …⁈
Through these, common judgment materials and judgment methods will be established.
Variation can be minimized.
These concepts are exactly the same as “process capability” in product manufacturing.
It is the same as assigning the process capability to each judgment material for the case.
Please see this page for details. “Variance and process capability”

