Characteristics and Selection of Copper for Machine Parts
Like Aluminum, I think that it is always touched copper (Cu) related products as much as I can say everyday.
I would like to explain how to select when actually using it in development design, together with the characteristics this time.
Chemical properties
Copper is widely used in general and its usage is various considering chemical properties.
But because of its features, I would like to talk about its chemical properties compared to the materials used for mechanical parts here.
Weight
The specific gravity of copper is about 120% of iron, about 200% of titanium, about 330% of aluminum and about 460% of carbon fiber.
Specific gravity of copper: 8.8 g / cm 3
In terms of weight, it is the heaviest among these, and there is no merit.
In order of specific gravity:
copper> iron> titanium> copper> carbon fiber
Weight is about 120% heavier than iron
Conductivity / thermal conductivity
It has high conductivity and thermal conductivity under normal circumstances.
It depends on the condition, but as you know it is very expensive.
I will compare and explain.
Conductivity
The electrical resistivity of copper is about 0.0003% of carbon fiber, about 4% of titanium, about 18% of iron and about 60% of aluminum.
Copper electric resistivity: 16.8 nΩ · m
Among the metals commonly used under normal temperature environment, copper has good electrical conductivity after silver.
Therefore, copper is used for general electric cables and electric wires.
Electrical resistivity order:
carbon fiber> titanium> iron> copper> copper
· Thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of copper is about 80% of carbon fiber, about 170% of aluminum, about 500% of iron, about 1900% of titanium.
Copper is used in many products that efficiently convey heat.
Copper thermal conductivity: 400 W / (m · K)
The order of thermal conductivity:
carbon fiber> copper> copper> iron> titanium
Of the metals that are normally used, the electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity are the best.
Chemical properties
· Corrosivity
Copper has low ionization tendency after gold, silver and is relatively strong against acid and alkali.
In the air, a copper oxide film gradually forms on the surface and the inside is protected, so there is no further corrosion progression.
In order of ionization tendency
copper> titanium> iron> copper
Magnetic
Copper is a diamagnetic body and when it applies a magnetic field, it is weak, but it will be the opposite magnetic only then at that time to repel its magnetic field.
Even if a magnet is attached, it is not magnetized.
Therefore, it is often used around sensors such as measuring instruments.
High corrosion resistance. There is no magnetism.
Mechanical properties
Copper is an essential part of mechanical parts by using mechanical properties.
I will explain what it is like.
Strength
Copper strength is somewhat inferior to iron.
Depending on the alloy, the specific strength of copper is the same as that of iron.
Therefore, considering the same volume, heavier copper will weaken the strength.
Processability
It is very soft and processability is bad with copper alone.
By making it a copper alloy, the processability is improved while taking advantage of the goodness of copper, and the application is wide. In the case of
Because of high thermal conductivity, warping and deformation are more likely to occur when processing than iron.
It is almost impossible in cutting, cutting and die punching, such as drawing, grinding, bending, welding, etc.
Copper can be easily cast.
Its melting point is lower than that of iron, so castability is high like iron.
However, since the coefficient of thermal expansion is a little high, distortion is likely to occur due to welding or the like.
Moreover, it is hard to heat local heating because of high thermal conductivity.
Processability is high, casting is relatively easy, but caution is also required for processing requiring heat
Price
It depends on circumstances and alloys, not everything applies, but it will be below.
In order of price per weight
carbon fiber> titanium> copper> aluminum> stainless steel> iron
Copper is widely used in various fields than features.
For that reason it is relatively expensive than others.
Copper is relatively expensive
Other
· Antibacterial
Copper is said to have antimicrobial properties.
It is said to inactivate a wide range of microorganisms by oxide film and chlorine compound generated on the surface.
· Color changes with aging
When placing copper in the air for many years, the color changes with time due to the influence of the oxide film generated on the surface.
It turns reddish brown → green and blue in about ten years.
Merits / Demerits Although it can be caught in either case, copper has a distinctive hue.
· Easy to recycle
Like aluminum, copper is easy to recycle.
It is easy to extract as copper alone, so it is recycled a lot.
· Very strong under low temperature environment
Copper does not become brittle even under low temperature environments.
Therefore, it is also used for superconducting materials and so on.
However, for copper and copper alloys that are usually used, let’s not use it in an environment where the temperature is high because its maximum temperature is about 300 degrees.
easy to recycle
At what time did you choose copper?
· I want to pass a lot of electricity per volume
Among the metals commonly used under normal temperature environment, copper is often used for electric cables and the like because it has good electrical conductivity next to silver.
However, when comparing per weight, aluminum conducts electricity.
I think that it is necessary to think by weight or volume.
· I want to convey fever efficiently
Copper has very good thermal conductivity as well as conductivity.
It is also often used for heat sinks and heat exchangers.
· I want to use it for parts of measuring equipment
Copper has diamagnetism, but it is not magnetized by the magnet.
Therefore, it is suitable for parts of measuring instruments that affect magnetic force.
· Want to use materials that can be maintained in low temperature environment
As I mentioned earlier, copper does not become brittle in very cold environments.
Therefore, it is strong even at low temperature.
However, let’s notice how to use because it is relatively weak in places like high temperature.
There are many others, too.
Copper is used in a wide variety of applications.
Please try variously in consideration of the situation depending on the situation.
It is the third most widely used material after iron and aluminum.
Because quality is stable, replacement design can be done comparatively easily.
Usage is diverse. Easy to replace
Below is a tumbler using the thermal conductivity characteristic of copper.
The cold thing is cold, and it is more tasty with the coldness feeling on the lip just before drinking.
和平フレイズ ラウンドロックタンブラー 380ml 燕三 純銅 EM-9606
Standard (alloy)
Copper alloy is copper based alloy.
Copper alloys are very common, for example Japanese coins other than 1 yen coin will be copper alloys.
Because copper is soft, it can be alloyed with manganese, tin, magnesium, zinc, nickel or the like to improve the properties as a metal material.
Copper alloys can roughly be roughly divided into a rolling (drawing) method and a casting method, as with aluminum, and are material specifications for each application.
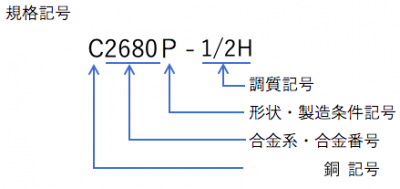
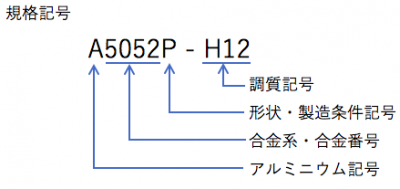
· Copper sign
It will be the initial letter C.
· Alloy · Alloy number
It will be the number of the alloy. The type of alloy is determined by the number at the head of this number.
· Shape · Manufacturing condition code
P: Plate, disc
PC: laminating board
H: Foil
FD: Die forged wrought goods
FH: Free dedicated goods
Such
– Condition symbol
F: Production as it is
O: Annealing
H: Work hardening
Such
Alloy of rolling (drawing) method
Here, we will explain the standard of “rolling (drawing) method” which is particularly frequently used.
Among the alloys of the rolling (drawing) method, there are non-heat treated alloys and heat treated alloys.
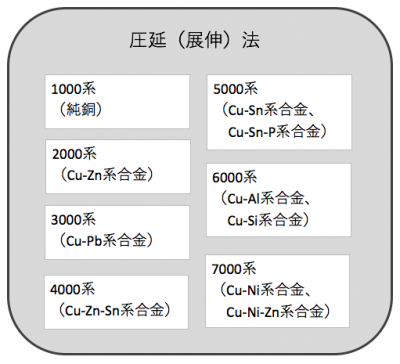
Copper alloy of the rolling method uses the name of the international copper alloy with a four-digit number.
Commercially available plate thickness is 0.3, 0.8, 1.0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 16, 18, 20, 22, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 mm is.
There are other board thicknesses, but it is easy to design, considering this too.
• 1000 series (pure copper)
When the copper purity is 99.9% or more, the electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity are good but the strength is low.
It is used as a conductive material or an aluminum foil, and it is not suitable as a structure or machine part.
C1020: Core wire of electric wire
· 2000 series (Cu – Zn alloy)
It becomes an alloy of copper and zinc.
Also referred to as brass or brass, it is most widely used among copper alloys.
Because of its good processability and beautiful, it is widely used, and it is also used for hardware.
Cracking may occur due to the residual stress at the time of processing, just by placing the alloy processed and so on.
This is a type of stress corrosion cracking, let’s design with internal stress taken into account during processing.
C2600: Connection terminal
C2680: Wiring equipment parts
• Series 3000 (Cu – Pb alloy)
It will be a copper alloy with lead added to improve workability.
It is also called free cutting brass.
C3560: Gear gear etc.
4000 series (Cu – Zn – Sn alloy)
2000 series (brass) with tin added.
Therefore, the resistance to corrosion in sea water has been increased more than brass.
Besides, it becomes an alloy which is resistant to stress corrosion cracking and abrasion.
C4250: Relays, switches
C 4621: Part for marine use
• 5000 series (Cu – Sn alloy, Cu – Sn – P alloy)
It is made by adding tin and phosphorus.
Also called phosphor bronze, it has strong strength and excellent spring properties.
Moreover, it is used for various things because it has good workability such as bending and drawing and high electric conductivity.
C 5191: wiring equipment parts etc.
• 6000 series (Cu – Al alloy, Cu – Si alloy)
6000 series such as C 6161 and C 6191 are made of aluminum bronze or brass for instrument valves, high strength brass
• 7000 series (Cu – Ni alloy, Cu – Ni – Zn alloy)
It becomes nickel plus it, it is also called white copper.
Also nickel plus zinc is also called western silver.
Since these colors become whitish, they are used as a substitute for silver from the appearance.
It is used for ornaments and tableware for beautiful things.
It also has strong corrosion resistance and seawater resistance.
C7351: Musical instrument
Copper has different characteristics in terms of color, corrosivity and conductivity depending on the alloy
Alloy of casting method
Below is the alloy standard of the casting method.
As a characteristic, it is almost the same as the alloy of the rolling (drawing) method, so it only lists the name.
“CAC” is attached to the name
CAC 101: pure copper system
CAC 201: Cu-Zn series
CAC 301: Cu-Zn-Al type
CAC 401: Cu-Sn series
CAC 502 A: Cu – Sn – P system
ACAC 602: Cu – Sn – Pb type
CAC 701: Cu-Al series
CAC 801: Cu – Zn – Si series
CAC 901: Cu-Sn-Bi type
Copper is used very much in various fields.
I think that a better copper alloy will be produced in the future.
Copper products are used as various processed products as follows.