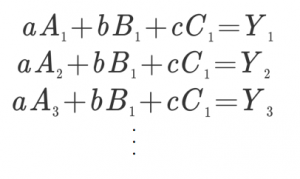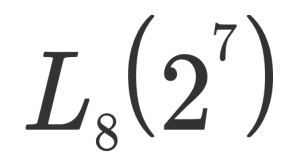Quality barometer of product function “Function reliability”
When designing products, we will make product specifications.
It will be expanded from the product specification to the function of the product, but as long as the quality of the function itself can not be maintained, the specification can not be satisfied as a result.
I would like to talk about how “functional reliability” is related to design.
When you want to increase functional reliability, please describe in concept of maintaining functions depending on functional reliability at design time It is necessary to make such change as it is.
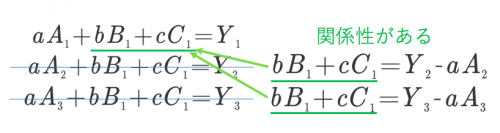
Relationship between specifications and functions
Before talking about “functional reliability”, I would like to talk about the relationship between function and specification in the first place.
As an example, I think with “knock type pen”.

As “Specification” “Take the pen tip out with just one hand’s thumb operation”
as “” feature “>” Press the upper part of the pen to tip the pen “, “
“Specification” should be
“Function” is a measure to make it appear as it should be from “specification”
I think that it is a relationship.
“Specification” means what it should be. “Function” means a strategy to make it appear
What is “functional reliability”?
“Functional reliability” is simply “quality of function almost” if it says simply.
I think with the “knock type pen” of the previous example.
The function was “When pressing the top of the pen the pen tip comes out” or “Press it once again” was.
“Function reliability”
10,000 times successfully “When the pen top is pressed, the pen tip comes out” and “When pressed once again” is satisfied.
.
This is the degree of whether the function itself can satisfy after expanding the function from the specification.
“Function reliability” ≈ “quality of function” → “quality of specification”
The quality of the function is as follows.
· Credit rating of function (functional confidence is strong here)
“Functional reliability” is the degree of satisfying the function developed from the specification
“Function reliability” What happens when you drop it?
As I mentioned earlier, “functional reliability” will lead to “quality of specifications”.
Degraded “functional confidence”
If it was a model change from an existing product, there should be not a few specifications that had been up to now.
Especially the specification on the extension of products up to now should have higher reliability than before.
If the reliability is low (when there are many failures that do not satisfy the specifications), customers will not be satisfied because what they thought as “what should be should be” is not satisfied.
It will not be satisfied even if there is a satisfactory part.
For the relationship between satisfaction and dissatisfaction, please see “satisfied / dissatisfied” .
“Function reliability” leads to “reliability” of the product itself.
Actually, it is only for that product, but despite the fact that customers tend to be confused with “reliability” of the whole company as a whole.
As a result, if “functional reliability” declines, and it is notified to customers, it will be regarded that “reliability” has declined for the entire company.
Even if it’s already sold or not, we will capture the “functional reliability” low at the end of “reliability”.
Maker’s way of thinking
Even if it is a manufacturer’s probability of failure (even if it is one in one million pieces), the customer who purchased and faced the problem was 100% defective item.
Therefore, in particular, Japanese manufacturing industry tends to increase “functional reliability”.
For that reason, we also manufacture products that incorporate process capability against product standards .
– Difference in concept of functional reliability by industry
“Function reliability” follows anything.
However, depending on the industry, the size of its reliability comes out to the market.
High functional reliability
Manufacturing industry
→ Because it was recalled and it takes a huge cost to rework
Feature reliability is relatively low
Service and software industry
→ Since it can be done with upgrading etc., it will not cost much for rework
If you do not judge “functional reliability”, the value of the enterprise will also decline.
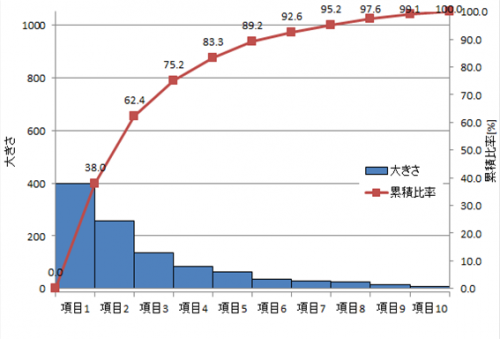
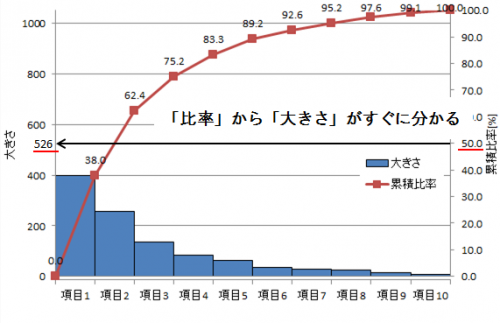
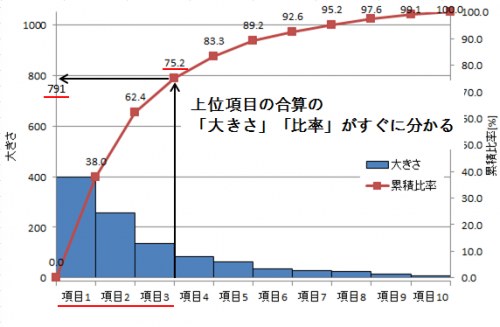
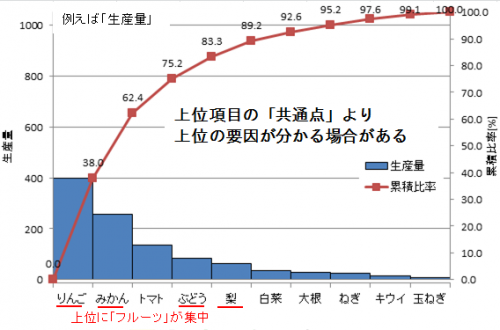
Bathtub curve (failure rate curve) grasping reliability trend
The failure rate trend is represented by a graph called bathtub curve (failure rate curve), in which the vertical axis shows “failure rate” and the horizontal axis shows “time lapse”.
Because it is a curve like a bathtub it is called a “bathtub curve”.
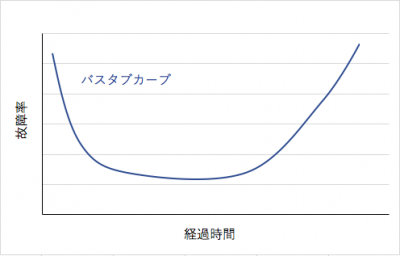
Over time, it is divided into an initial failure period, a random failure period, and a wear failure period.
Failure rate constant curve (CFR)
Failure rate increase curve (IFR)
When the tendency of failure rate decrease curve (DFR) is large
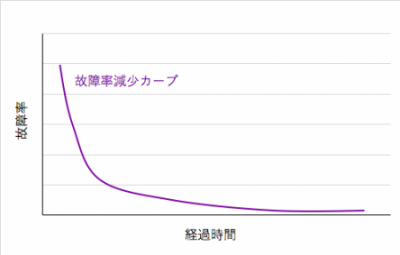
It is a failure due to defects in manufacturing.
This tendency is likely to occur even if it is due to the quality that does not have the inspection process or is missing.
This type of failure rate decreases with the passage of time.
When the tendency of the failure rate constant curve (CFR) is large

It is a failure that happens by chance.
It is a related breakdown when the range of the standard is too sweet or when the use range of the product exceeds the assumed value.
It is of a type that does not relate to time and breaks down at a certain rate.
When the tendency of failure rate increase curve (IFR) is large
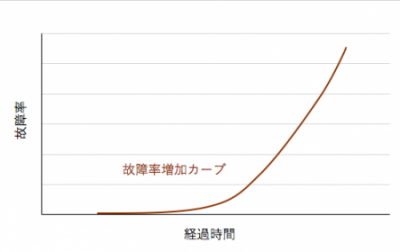
The position of this curve will change due to changes in design, material etc.
It is a type of mechanical failure such as wear that increases with the passage of time.
These three graphs together form a bathtub curve.
If you are forced to take a model change or countermeasure, it is easier to respond if you judge which trend is strong and respond.
Especially it is better to judge which function will be a strong curve
It is an easy-to-understand book as a judgment of quality engineering and function. Those who want to refer about function and quality please.
これでわかった! 超実践 品質工学 ~絶対はずしてはいけない 機能・ノイズ・SN比の急所~
Measures to improve reliability
Reliability may not be improved due to various factors.
There may be cases where reliability may not be improved due to human error such as “human error” or crossing the “planning” “design” “manufacturing” department.
Contents of reliability improvement
“Alternative” not to induce mistakes
“Simplify” not causing mistakes
Detecting mistakes “Detecting abnormalities”
“Corresponding deployment” not to disseminate mistakes
Make no mistakes “exclusion”
Do not make the cause of mistakes, if you eliminate it in any way.
Do not trigger mistakes “Alternatives”
To avoid making a mistake, it is to substitute with another thing so as not to be difficult.
Do not make mistakes “simplify”
It is to simplify work items and make the mistake as few as possible.
· Notice of mistakes “Detect anomalies”
It is a method to notice the mistake by stopping the abnormality discovery device, inspection, etc. and stop it.
· Do not disseminate mistakes “Corresponding deployment”
It is to make similar mistakes not to happen elsewhere.
Although we need to think about these, we need to do “risk assessment” on top of that.
What is the risk assessment here when it becomes unreliable? It is something to think about.
Quality standards will also vary depending on the country and purchasing layer. Therefore, the risk assessment will also differ.
These ideas are the same as risk assessment .
Let’s do risk assessment and design corresponding to it. For details, please look over there.
The risk assessment will be different as I mentioned earlier.
I think that it is good if we start out measures and investigate the contents of evaluation beforehand by the method using the tool etc. described later.
As for the function, we also have to do risk assessment
The important part is “Redundancy”
Risk assessment, but still very important parts need to be “redundant” (duplicated).
“Redundancy” is a circuit or system that operates without problems even if one of the functions is duplicated and the other remains even if one of them fails.
This is a very good method as a way to increase functional reliability. However, the cost is double that amount.
In this way, a dual circuit system with backup is used in many places.
· Power plant
· Financial system
· Safety circuit
etc
Depending on risk assessment, redundancy must be selected
Tool for identifying countermeasures
As mentioned in the section on measures to improve reliability, quality standards will also vary depending on the country and purchasing layer.
Change point analysis for prevention (DRBFM)
Failure analysis from component failure (FMEA)
Failure cause analysis (FTA)
It will become clear if you make full use of it.
For details, I would like to explain it in the case of the contents of each item.
Use tools to clarify and lead to risk assessment
An easy-to-understand book of quality engineering is here.
Please click here if you would like to refer.